The Keystone site
The Keystone archaeological site is situated within the confines of the Keystone Heritage Park. The site is owned by the City of El Paso and the Archaeological Conservancy. It is recognized as a Texas State Archaeological Landmark, and is one of 17 such properties in El Paso County that are under the jurisdiction of the Texas Historical Commission. The Keystone Heritage park was created to help protect and preserve this archaeological site, and to enhance public awareness concerning the ancient inhabitants of El Paso County.
The Archaic Period
The Keystone archaeological contains some of the oldest human-made structures identified in the U.S. Southwest, dating back more than 4,500 years. In fact, there is no other archaeological site in the region that contains as many ancient houses dating from this period, known as the Middle Archaic. The early inhabitants of this time are referred to as Paleoindians, and they lived during a time of transition from the Ice Age to the modern climatic regime.
Survival in the Archaic Period
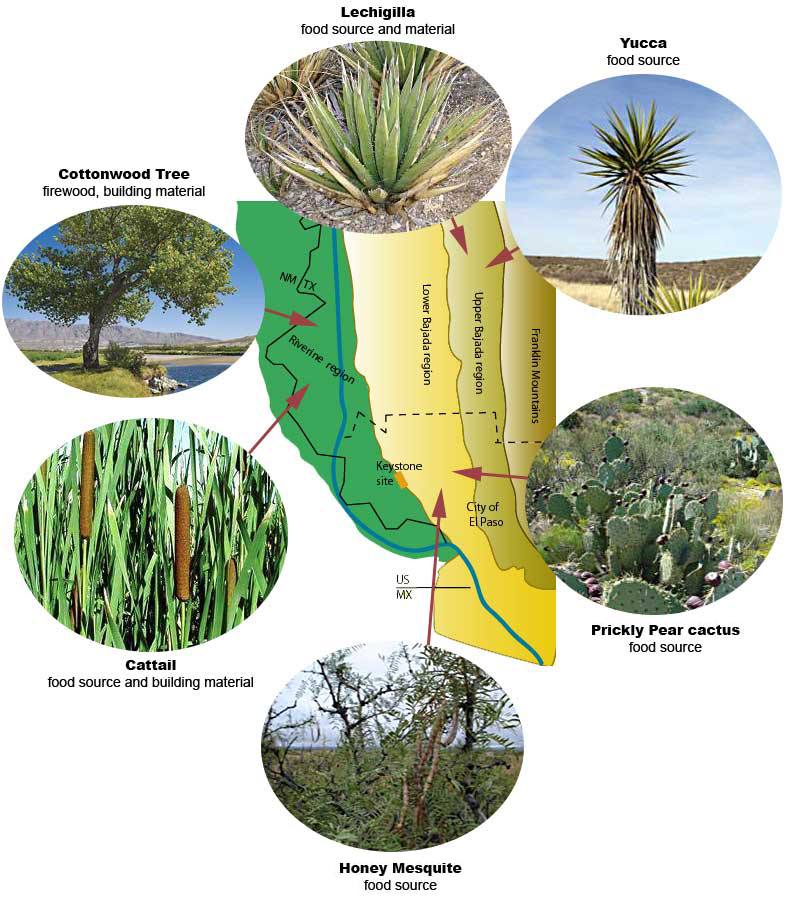
As hunter-gatherers the Archaic inhabitants of Keystone, lived in small, mobile family groups and moved in response to the seasonal availability and distribution of wild plants and animals. Many of these were found in the various ecosystems in the El Paso region. These regions are the; Riverine region, Franklin Mountains, and the Upper and Lower Bajada (mountain fronts) regions. Each of these landform areas had resources that were used by the inhabitants of Keystone for food, tools, and building material.